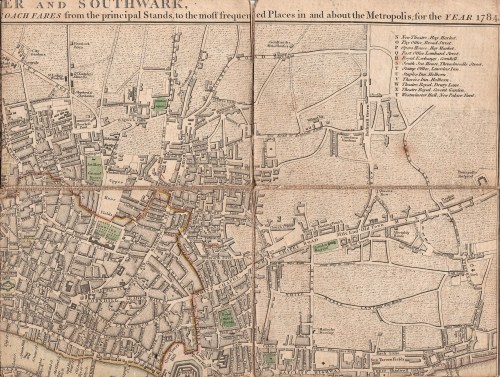
I love this print of 1796, “View of the Monument” published by L. Stockdale of Piccadilly. I’ve cropped it to focus in on the street scene in more detail and it is fascinating to go to Google Streetview and look down Fish Street Hill today past the Monument to the distinctive tower of St Magnus the Martyr. You can just make out its clock which used to overhang the beginning of London Bridge before the old bridge was demolished and moved a short distance upstream. The modern view includes a glimpse of the top of the Shard which would have amazed the Georgian Londoner!

This image is so full of wonderful details. London Bridge is still the medieval Old London Bridge, shorn of its shops and houses and with little alcoves all along it so that pedestrians could take refuge from heavy vehicles coming over. (Westminster Bridge had similar alcoves and James Boswell, ever on the look-out for somewhere novel for a bit of nooky, records having sex in one). It was so narrow that it had men controlling an alternating traffic flow system and most stage coaches stopped in Southwark on the other bank rather than fight their way over.
The way the pavements sit on little sloping ‘banks’ above the roadway was new to me and I like the bollards to keep wheeled traffic off them – there’s even a re-used cannon on the left. The road is lined with shops and the shoppers are probably respectable middle class – merchant and professional families rather than the high society of Mayfair and St James’s to the west. This is the City, after all. There are also porters with loads on their backs, one on each side of the street, and a woman with her basket of wares on her head.
In February last year I posted “Looking Down on London Bridge” with more about St Magnus the Martyr. Walk 8 in my Walking Jane Austen’s London will take you from Temple Bar, through the City, down Fish Street Hill and onto London Bridge. Alternatively Walk 10 in Walks Through Regency London will guide you down Fish Street Hill, over London Bridge and into Southwark.














 Mr George Wood lived in Blandford Court which was on the south side of Pall Mall behind Marlborough House which is within a five minute walk of Hoby’s shop which is probably why the invoice appears to have been hand-delivered. I suspect that Mr Wood was a relative of Lieutenant-General Sir George Wood, ” the Royal Bengal Tiger” and his brother Sir Mark Wood, bt. Sir Mark certainly lived in Pall Mall.
Mr George Wood lived in Blandford Court which was on the south side of Pall Mall behind Marlborough House which is within a five minute walk of Hoby’s shop which is probably why the invoice appears to have been hand-delivered. I suspect that Mr Wood was a relative of Lieutenant-General Sir George Wood, ” the Royal Bengal Tiger” and his brother Sir Mark Wood, bt. Sir Mark certainly lived in Pall Mall.

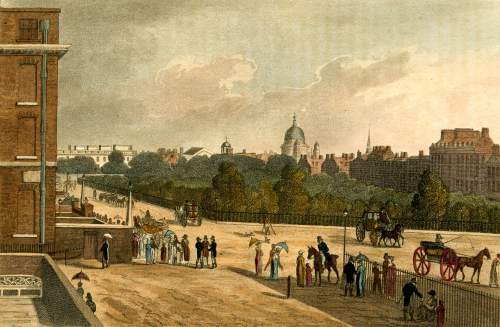


 Fagan (above, in a self-portrait with his second wife Maria Ludovica’ Flajani depicted ‘à la Greque’ 1803) eventually fell out of favour with the court and found himself increasingly in debt. He returned to Rome and in 1816 committed suicide by jumping from a window. His widow managed to sell his Roman collection to the Vatican museums but in Sicily the authorities seized his possessions to prevent their export. In 1819 the “Fagan Marbles” were purchased by the Museum of the Royal University and remain as an intact collection, now in the Palermo museum. As the display in the museum today notes, this was a turning point in awareness of the importance of retaining materials from different sites together and raised the consciousness of Sicily’s archaeological treasures.
Fagan (above, in a self-portrait with his second wife Maria Ludovica’ Flajani depicted ‘à la Greque’ 1803) eventually fell out of favour with the court and found himself increasingly in debt. He returned to Rome and in 1816 committed suicide by jumping from a window. His widow managed to sell his Roman collection to the Vatican museums but in Sicily the authorities seized his possessions to prevent their export. In 1819 the “Fagan Marbles” were purchased by the Museum of the Royal University and remain as an intact collection, now in the Palermo museum. As the display in the museum today notes, this was a turning point in awareness of the importance of retaining materials from different sites together and raised the consciousness of Sicily’s archaeological treasures.


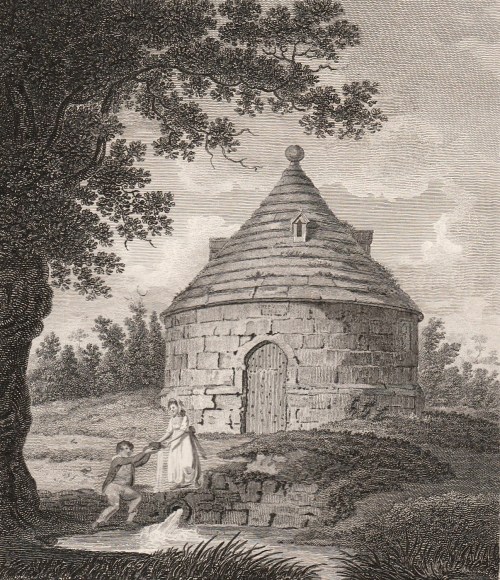
 At first I thought the gentleman was presenting his lady with a flower, but if you look carefully, it is a cutting with the correct slanted cut at one end. I can’t decide whether she is as fascinated by horticulture as he obviously is, or disappointed with the offering!
At first I thought the gentleman was presenting his lady with a flower, but if you look carefully, it is a cutting with the correct slanted cut at one end. I can’t decide whether she is as fascinated by horticulture as he obviously is, or disappointed with the offering!








