
The Earl of Wittering marshals his family after breakfast to decide on the morning’s activities. ‘Porrett has made a recce,’ he announces. (He commanded the local militia for four months and, in his imagination, is forever a soldier…) ‘The bath house is up to standard and there is the choice of taking a machine and having a dunking or using the facilities – plunge pools, shower baths, steam rooms and so forth.’
‘I would like to go in the sea,’ young Arthur announces. ‘I will search for marine life.’
‘In that case Porrett will accompany you.’
Porrett attempts to look delighted at the challenge and not like a man who has already been in the sea once that morning.
‘I will bathe too,’ says Emily casting Porrett a languishing look. ‘I am already quite over-warm.’ Quite how she proposes to get close to Porrett once in the water she has no idea, but pretending to drown might be a good start…
‘Over-warm’ is putting it mildly so far as her grandfather’s besotted secretary is concerned. The sea, he fears, will probably boil around him if she is in it too.
‘I intend sampling the warm bath,’ Lady Wittering announces. ‘You will no doubt wish to join me, Emilia,’ she adds to her daughter in law in clear command.
‘I’ll investigate the billiards room. May try a shower later,’ Viscount Ditherstone remarks. If nothing else, Porrett thinks, the wretched man will be investigating just how separate the male and female facilities are.
‘And I will go for a dunking, I suppose,’ the Earl grumbles. ‘No need for you after all, Porrett, so long as I’m with Arthur.’ Fortunately he does not see the expression on his granddaughter’s face. ‘We’ll go in fifteen minutes.’
The family is completely delighted with the facilities of the bath house (except for Emily, who is still sulking). The two older ladies take themselves off to the warm baths where Lady Ditherstone, at least, imagines herself as a beauteous Roman lady about to bathe in asses’ milk –

The bathers, Emily chaperoned by her very reluctant maid, troop downstairs to their respective bathing machines and Porrett trails after the Viscount into the billiards room. He is not going to succumb to the temptation to take one of the telescopes out onto the balcony, he tells himself as he fidgets around, glancing at the well-stocked selection of newspapers and journals while keeping half an ear cocked for the click of billiard balls.
Silence, except for the snores of some elderly gentleman over by the bookshelves. Ditherstone has vanished. Porrett hastens out. Goodness knows what trouble the amorous lord is about to get himself into. No-one is visible in the vestibule but the faint click of boot heels comes from the steps under an arch labelled Ladies’ Rooms. With true valour Porrett rushes down in pursuit, just as a piercing shriek echoes up. In front of him is a door labelled Shower Bath. It is open and just visible are the tips of Lord Ditherstone’s brown tail coat. Porrett seizes them in both hands, drags backwards and yanks the door closed, finding himself embracing an armful of very irritated Viscount.

‘Thank Heavens, my lord! You had wandered into the ladies’ section in error,’ he gasps, somewhat impeded by an aristocratic elbow in the stomach as the Viscount storms back upstairs. ‘Really,’ he adds severely to the gawping attendants as they reach the vestibule, ‘You should ensure the notices are more legible. His lordship has just been severely discommoded, as might any gentleman, especially a scholar such as his lordship with weak eyesight.’ The Viscount has occasionally been known to glance at the sporting press but that is as far as his scholarship extends.
‘Coffee and brandy,’ Ditherstone demands. ‘In the billiards room, immediately.’ Porrett follows him, fearing instant dismissal, and finds his hand taken and wrung in a painful clasp. ‘Good man, quick thinking. Two cups and glasses,’ he snaps as the waiter comes in. ‘Mr Porrett will be joining me.’ All Porrett can feel is intense relief that he will not be forced to leave the household, forced to say goodbye to Emily for ever…
The photograph at the top of the post is of the Greek Revival-style bath house at Ilfracombe. This was a popular style intended to create a link with the Classical world and impart intellectual respectability to the pleasures of the bath. The two other images are from Poetical Sketches of Scarborough (1813).
Discover more about the Georgian bath houses – the gyms and fitness clubs of their day in The Georgian Seaside
Next time the family take some exercise on the beach.
Save
Save
Save
Save
Save
Save
Save





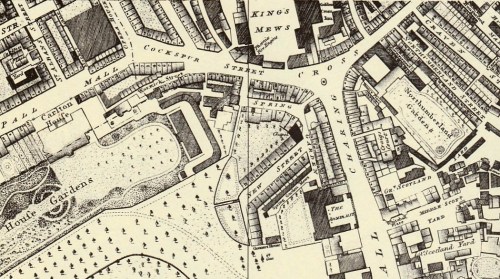




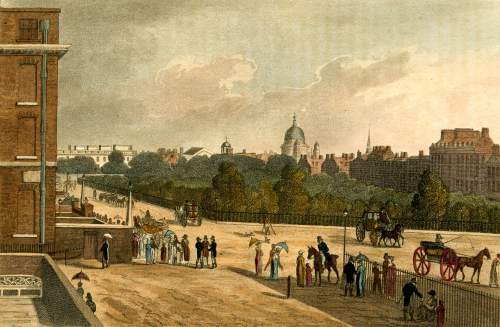



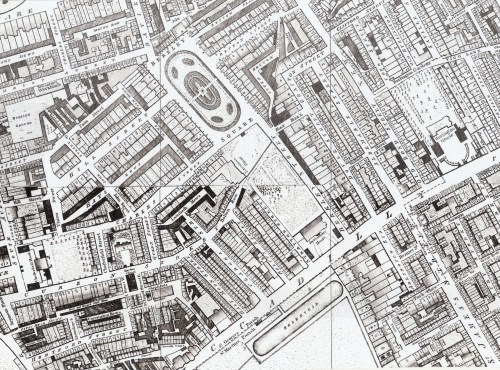

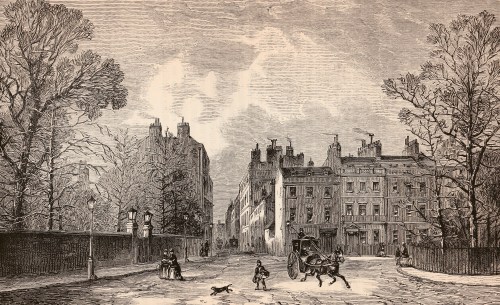
 In 1717 the 2nd Earl of Oxford, Edward Harley, began work on the development of his estates north of “the road to Oxford” or Tyburn Road, that eventually became Oxford Street. The first element in his grand design was Cavendish Square, named for his wife Lady Henrietta Cavendish Holles. The Duke of Chandos bought the entire northern side for a mansion (described by Ackermann’s as a ‘palace’), Lord Harcourt and Lord Bingley bought sites on the east and west and the rest was sold to speculative builders. Work was interrupted by the financial crisis of the South Sea Bubble in 1720 but the Earl persisted, developing streets and Oxford Market to stimulate interest in his scheme.
In 1717 the 2nd Earl of Oxford, Edward Harley, began work on the development of his estates north of “the road to Oxford” or Tyburn Road, that eventually became Oxford Street. The first element in his grand design was Cavendish Square, named for his wife Lady Henrietta Cavendish Holles. The Duke of Chandos bought the entire northern side for a mansion (described by Ackermann’s as a ‘palace’), Lord Harcourt and Lord Bingley bought sites on the east and west and the rest was sold to speculative builders. Work was interrupted by the financial crisis of the South Sea Bubble in 1720 but the Earl persisted, developing streets and Oxford Market to stimulate interest in his scheme. the Bason and the gravel workings to the north had completely vanished under streets and houses and the whole square had been developed as can be seen in the map to the right.
the Bason and the gravel workings to the north had completely vanished under streets and houses and the whole square had been developed as can be seen in the map to the right.








 Emily gives him a beaming smile, much restored by thoughts of shopping, as they reach the circulating library. Porrett, having established that the monthly subscription is eight shillings, deals with the business side, taking out a subscription for both senior ladies. He also subscribes for himself, for he has a secret penchant for poetry and intends to take a slim volume off to the garden where he can brood on his heartache in peace. (Above, the artist of a Regency ‘bat print’ bowl has caught Porrett immersed in his poetry next to a beehive.)
Emily gives him a beaming smile, much restored by thoughts of shopping, as they reach the circulating library. Porrett, having established that the monthly subscription is eight shillings, deals with the business side, taking out a subscription for both senior ladies. He also subscribes for himself, for he has a secret penchant for poetry and intends to take a slim volume off to the garden where he can brood on his heartache in peace. (Above, the artist of a Regency ‘bat print’ bowl has caught Porrett immersed in his poetry next to a beehive.)